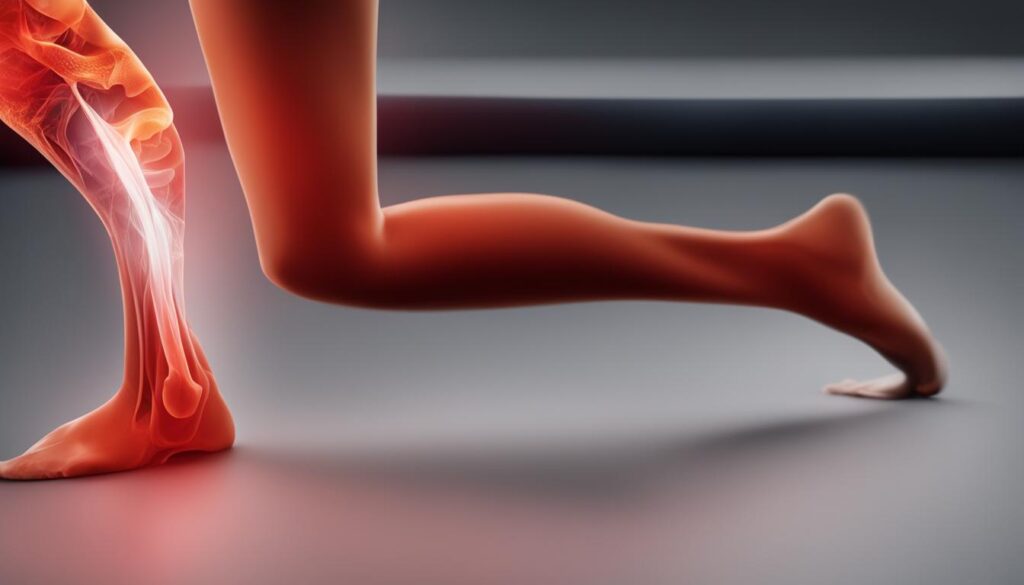
Leg cramps and diabetes are two conditions that may seemingly have no connection, but research suggests otherwise. Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a complex disease characterized by persistent high blood sugar levels. It primarily affects the body’s ability to produce or respond to insulin, leading to various complications throughout the body. Leg cramps, although not exclusive to diabetes, are commonly observed in individuals with this condition. In this article, we explore the correlation between leg cramps and diabetes, the potential causes, and effective management strategies.
Key Takeaways:
- Diabetes mellitus is characterized by persistent high blood sugar levels and can lead to various complications.
- Leg cramps are a relatively common manifestation in individuals with diabetes.
- Potential causes of leg cramps in diabetes include electrolyte imbalances, hypoglycemia, peripheral vascular disease, and peripheral neuropathies.
- Diabetic neuropathy is a condition associated with nerve damage due to long-term high blood sugar levels, which can contribute to leg pain and cramps.
- Managing blood sugar levels and implementing lifestyle changes can help alleviate leg cramps associated with diabetic neuropathy.
Understanding Diabetic Neuropathy and Leg Pain
Leg pain and cramps in people with diabetes are often a result of diabetic neuropathy. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy is a condition where nerve damage occurs due to long-term high blood sugar levels. Symptoms of diabetic neuropathy may include pain, burning, tingling, and numbness.
Managing blood sugar levels is crucial to help alleviate and prevent leg pain and cramps associated with diabetic neuropathy. By controlling high blood sugar levels, individuals can reduce the risk of nerve damage and minimize symptoms of diabetic neuropathy.
In addition to blood sugar control, other treatment options for diabetic neuropathy and leg pain include:
- Medications: Pain medications or nerve pain medications, such as gabapentin or pregabalin, may be prescribed to help manage symptoms.
- Physical therapy: Special exercises and physical therapy techniques can improve strength, flexibility, and overall muscle function, reducing leg pain.
- Lifestyle changes: Making healthy lifestyle choices, such as regular exercise, maintaining a balanced diet, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption, can effectively manage leg pain.
- Supportive devices: Wearing support stockings or using braces or orthotic devices can provide relief by reducing pressure on the affected nerves and muscles.
- Complementary therapies: Techniques such as acupuncture, massage, and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) may help alleviate leg pain and improve overall well-being.
- Alternative treatments: Some individuals find relief through alternative therapies like herbal remedies, essential oils, or mindfulness practices. However, it is important to consult a healthcare professional before trying any alternative treatments.
Remember, every individual’s experience with diabetic neuropathy and leg pain may be different. It is essential to work closely with your healthcare team to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses your unique needs and minimizes discomfort.

Managing Leg Pain and Cramps in Diabetic Neuropathy
Managing leg pain and cramps in diabetic neuropathy requires a comprehensive approach that addresses both the underlying condition and its symptoms. By implementing various strategies, individuals with diabetic neuropathy can find relief from leg pain and cramps and improve their overall quality of life.
To effectively manage leg pain and cramps in diabetic neuropathy, it is crucial to keep blood sugar levels within the target range. Maintaining stable blood sugar levels helps minimize nerve damage and reduce the severity of symptoms.
Treating Leg Pain and Cramps
Pain management is an essential component of leg pain and cramp management in diabetic neuropathy. Several options are available for pain relief:
- Medication: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can help alleviate mild to moderate pain. In some cases, prescription medications like duloxetine or pregabalin may be prescribed by a healthcare provider to manage more severe pain.
- Dietary supplements: Certain dietary supplements may offer some relief from leg pain and cramps. Alpha-lipoic acid, acetyl-L-carnitine, vitamin B-12, and vitamin D have shown potential in reducing neuropathic pain. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement.
- Home remedies: Alongside medical treatments, home remedies can complement leg pain and cramp management. Physical therapy exercises, such as stretching and strengthening exercises for the legs, can help improve muscle function and reduce symptoms. Soaking in warm baths and applying heat or cold packs to the affected area may also provide temporary relief.
It is important to note that every individual’s experience with leg pain and cramps in diabetic neuropathy may vary. Consulting with a healthcare provider is crucial to create a personalized treatment plan that addresses specific needs and considerations.
Regular Monitoring and Adjustment of Treatment
Managing leg pain and cramps in diabetic neuropathy requires ongoing monitoring and adjustment of treatment strategies. Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare professionals are vital to assess the effectiveness of the current treatment plan and make any necessary adjustments.
Additionally, individuals should report any changes in leg pain or cramp frequency and severity to their healthcare provider promptly. This enables healthcare professionals to identify potential complications and make informed decisions regarding changes to the treatment plan.
Preventing and Monitoring Leg Pain in Diabetes
Preventing leg pain in diabetes is crucial for maintaining overall health and quality of life. By adopting certain preventive measures and monitoring leg pain symptoms, individuals with diabetes can minimize the risk of complications and improve their well-being.
Regular Exercise for Improved Blood Flow
Regular exercise plays a significant role in preventing leg pain and cramps in diabetes. Engaging in physical activities that promote blood flow can help strengthen leg muscles, improve circulation, and reduce the likelihood of experiencing discomfort. Simple exercises, such as walking, jogging, cycling, and swimming, can be beneficial in preventing leg pain and promoting overall cardiovascular health.
| Benefits of Regular Exercise for Leg Pain Prevention in Diabetes | |
|---|---|
| 1. | Enhances blood circulation to the legs and feet |
| 2. | Strengthens leg muscles, reducing strain on nerves |
| 3. | Helps control blood sugar levels and reduces the risk of peripheral neuropathy |
| 4. | Improves overall cardiovascular health and lowers the risk of complications |
Monitoring Leg Pain Symptoms and Seeking Medical Attention
Monitoring leg pain symptoms is essential for individuals with diabetes. Regularly assessing the severity, frequency, and duration of leg pain or cramps can help identify any changes or potential complications. If leg pain becomes persistent or worsens, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly. Healthcare providers can evaluate the symptoms, perform necessary tests or assessments, and provide appropriate guidance and treatment options.
Prevention of Diabetic Neuropathy and Underlying Conditions
Preventing leg pain in diabetes also involves taking measures to prevent diabetic neuropathy and other underlying conditions. Maintaining stable blood sugar levels through proper diabetes management is key. This includes following a healthy diet, taking prescribed medications as directed, and monitoring blood sugar levels regularly. By managing diabetes effectively, the risk of developing leg pain and cramps associated with diabetic neuropathy can be significantly reduced.

In conclusion, preventing leg pain in diabetes requires a proactive approach that includes regular exercise, monitoring symptoms, and managing diabetes effectively. By adopting these strategies, individuals with diabetes can reduce the risk of leg pain and cramps, improve blood flow, and maintain overall well-being.
Link Between Muscle Cramps and Diabetes
Muscle cramps are a common complication of diabetes, often caused by various factors such as electrolyte imbalances, hypoglycemia, peripheral vascular disease, and peripheral neuropathies. In some cases, individuals with poorly controlled diabetes may experience a rare condition called muscle infarction.
Diabetes can also lead to several musculoskeletal effects, including loss of deep tendon reflexes, peripheral neuropathy, reflex sympathetic dystrophy syndrome, neuropathic joints, carpal tunnel syndrome, adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder, tenosynovitis, diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis, and Dupuytren’s contracture.
Muscle cramps in diabetes can be uncomfortable and interfere with daily activities. It is important for individuals with diabetes to work closely with their healthcare providers to manage their condition and prevent or alleviate muscle cramps.
| Complication | Description |
|---|---|
| Peripheral Neuropathy | Damage to the peripheral nerves, leading to numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness |
| Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy Syndrome | A disorder characterized by excessive pain and abnormal swelling in response to an injury |
| Neuropathic Joints | Joint deformities caused by nerve damage and loss of sensation |
| Carpal Tunnel Syndrome | Nerve compression in the wrist, resulting in hand and arm pain |
| Adhesive Capsulitis of the Shoulder | Stiffness and pain in the shoulder joint, limiting range of motion |
| Tenosynovitis | Inflammation of the tendon sheath, causing pain and swelling |
| Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis | An overgrowth of bone that can limit movement and cause pain |
| Dupuytren’s Contracture | The thickening and tightening of connective tissues in the hand, leading to hand deformities |
Treatment Options for Muscle Cramps in Diabetes
Treatment options for muscle cramps in diabetes vary depending on the underlying cause. It is important to address the root cause of the muscle cramps to effectively alleviate the symptoms. Here are some treatment options to consider:
1. Pain Management
One approach to managing muscle cramps in diabetes is through pain management techniques. Over-the-counter pain relievers can provide temporary relief from muscle cramps. Additionally, muscle relaxants prescribed by a healthcare professional may help relax the muscles and provide relief.
2. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can be an effective treatment for muscle cramps in diabetes. A physical therapist can help develop a tailored exercise program that focuses on stretching and strengthening the muscles, promoting flexibility, and reducing the frequency and intensity of muscle cramps.
3. Lifestyle Changes
Implementing lifestyle changes can play a significant role in managing muscle cramps in diabetes. Maintaining a healthy diet rich in nutrients such as potassium, magnesium, and calcium can help prevent electrolyte imbalances that can contribute to muscle cramps. Regular exercise, such as walking or swimming, can also improve muscle function and reduce cramp occurrences.
4. Blood Sugar Control
Controlling blood sugar levels is crucial in managing muscle cramps associated with diabetes. Consistently monitoring and managing blood sugar levels through medication, diet, and lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk of muscle cramps and other diabetes-related complications.
Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance on the most suitable treatment options for muscle cramps in diabetes.
| Treatment Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Pain Management | Involves the use of over-the-counter pain relievers and prescribed muscle relaxants to alleviate muscle cramps. |
| Physical Therapy | A tailored exercise program focusing on stretching and strengthening muscles to reduce the frequency and intensity of muscle cramps. |
| Lifestyle Changes | Includes maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, and preventing electrolyte imbalances that can contribute to muscle cramps. |
| Blood Sugar Control | Monitoring and managing blood sugar levels through medication, diet, and lifestyle changes to prevent muscle cramps and other diabetes-related complications. |
The Importance of Early Detection and Prevention
Early detection plays a vital role in preventing the development of serious foot and leg conditions associated with diabetic neuropathy. Regular monitoring and prompt reporting of symptoms to healthcare providers are crucial for identifying potential complications at an early stage.
By actively managing blood sugar levels and following a comprehensive treatment plan, individuals with diabetes can significantly reduce the risk of lower leg amputations and other diabetic neuropathy complications.
“Early detection is key in managing the effects of diabetic neuropathy. By identifying and addressing symptoms early on, we can implement preventive measures and reduce the severity of potential complications.”
Diabetic neuropathy can lead to various foot and leg conditions, including ulcers, infections, and Charcot foot. Detecting these issues early allows for timely interventions, such as wound care, antibiotics, and orthopedic interventions, which can prevent further damage and improve overall outcomes.
Additionally, proper foot care and regular inspections can help identify any changes in foot structure, skin integrity, or sensation. Taking proactive steps to prevent injuries, such as wearing appropriate footwear and practicing proper foot hygiene, can significantly reduce the risk of complications.
Early Detection Symptoms
Early signs of diabetic neuropathy and related foot and leg conditions may include:
- Numbness or tingling in the feet
- Burning or shooting pain in the legs
- Loss of balance or coordination
- Changes in foot shape or structure
- Foot ulcers or open sores that do not heal
- Infections or slow wound healing
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider promptly for further evaluation and appropriate management.
Preventive Measures
Prevention plays a key role in managing diabetic neuropathy complications and reducing the risk of lower leg amputations. Here are some preventive measures:
- Strict blood sugar control through a combination of medication, diet, and regular exercise
- Regular foot inspections and self-care practices, including daily washing, moisturizing, and checking for any abnormalities
- Proper footwear selection that provides adequate support and cushioning
- Avoiding activities that may cause foot injuries or trauma
By adopting these preventive measures and adhering to a comprehensive care plan, individuals with diabetes can actively manage their condition and minimize the risk of diabetic neuropathy complications.
In conclusion, early detection and prevention are crucial in managing diabetic neuropathy and preventing serious foot and leg conditions. By staying vigilant, seeking prompt medical attention, and implementing preventive measures, individuals with diabetes can significantly reduce the risk of lower leg amputations and improve their overall quality of life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the link between leg cramps and diabetes is particularly evident in the context of diabetic neuropathy. Diabetic neuropathy can lead to leg pain and cramps as a result of nerve damage caused by high blood sugar levels. To alleviate these symptoms, it is crucial to focus on managing blood sugar levels effectively. This can be achieved through the use of prescribed pain medication, dietary supplements, and implementing lifestyle changes.
By taking proactive measures to control blood sugar levels, individuals with diabetes can experience relief from leg pain and cramps associated with diabetic neuropathy. It is also important to emphasize the significance of early detection and prevention in order to avoid potential complications and enhance overall quality of life for those living with diabetes.
With the implementation of a comprehensive treatment plan that prioritizes blood sugar control, individuals can effectively manage leg cramps and diabetic neuropathy. By being proactive in monitoring symptoms, addressing pain, and making lifestyle adjustments, individuals can significantly improve their overall well-being and lead a more comfortable life.
FAQ
Is there a link between leg cramps and diabetes?
Yes, there is a link between leg cramps and diabetes, particularly in the context of diabetic neuropathy. Diabetic neuropathy can cause leg pain and cramps due to nerve damage resulting from high blood sugar levels.
What causes leg cramps in diabetes?
Leg cramps in diabetes can be caused by electrolyte imbalances, hypoglycemia, peripheral vascular disease, and peripheral neuropathies.
How can leg pain and cramps in diabetic neuropathy be managed?
Managing leg pain and cramps in diabetic neuropathy involves keeping blood sugar levels within target range, taking pain medication as prescribed, using dietary supplements, and implementing lifestyle changes such as regular exercise and hot baths.
Can leg pain and cramps in diabetes be prevented?
Leg pain and cramps in diabetes can be prevented by maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise to promote blood flow, and monitoring symptoms of diabetic neuropathy.
What are the complications of diabetes related to muscle cramps?
Complications of diabetes related to muscle cramps include muscle infarction, loss of deep tendon reflexes, peripheral neuropathy, reflex sympathetic dystrophy syndrome, neuropathic joints, carpal tunnel syndrome, adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder, tenosynovitis, diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis, and Dupuytren’s contracture.
How are muscle cramps in diabetes treated?
Treatment options for muscle cramps in diabetes depend on the underlying cause and may include pain management techniques, muscle relaxants, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise.
Why is early detection and prevention important in diabetes?
Early detection and prevention of diabetic neuropathy and leg cramps are essential to prevent the development of serious foot and leg conditions and reduce the risk of lower leg amputations.